
Admin Name
10 months ago
admin
#haematology
Sickle Cell Disease
SubsetsSickle Cell Trait:HbSA (± 10% population) Heterozygocity for HbS (sickle cell trait): usually asymptomatic, lower parasitemia, higher Hb
Sickle Cell Disease:
HbSS (<1% population) Homozygocity for HbS or HbS+C/β: change in Hb structure, sickling if deoxygenated
Making the Diagnosis
- There is a wide spectrum of severity
- Suspect if patient is chronically anaemic and/or received a previous transfusion (>2 months of age)
- Suspect in children who have suffered from one or more of the presentations or complications listed below
- "Sickle cell test"
- sickledex or shaketest (>12 months) available at main lab
- Hb-electrophoresis: quantifies fraction of Hb-types. Often available at sickle clinic.
- Transfusions
- Painful crises
- Infections
- Episodes of Jaundice
- Family history (autosomal recessive disease)
- Provoking events: De-oxygenation:
- Infection
- General anaesthesia & surgery
- Dehydration
- Hypo- and hyperthermia
- Extreme physical exercise
- Altitude
- Smoking/ smoky rooms
- Vital signs (including blood pressure and oxygen saturations)
- Pallor/ Jaundice
- Chest, heart
- (Hepato-) splenomegaly (or absence)
- Bone tenderness, deformities and frontal bossing
- PCV and MPS
- FBC + red cell morphology to look for characteristic sickle cells
- Reticulocytes
- Blood culture if febrile
- Further tests guided by complaints (e.g. X-ray/ abdominal ultrasound/ CT-scan/ LP)
- Severe (PCV<12%) Anaemia
- Moderate (PCV>12%) see Prevention in Anaemia chapter
- If shocked consider splenic sequestration (Give 10ml/ kg Normal Saline Shock protocol)
- Suspect Parvovirus B19 infection if aplastic
- Transfuse in acute chest syndrome or stroke
- Oxygen: Oxygen stops the sickling of RBC's. All children presenting with a Sickle Cell Crisis should be started on Oxygen, even if saturations are normal
- Fluids:
- Per 24 hrs give 1.5 x maintenance fluid IV
- e.g. 24kg
- 1.5 x (10x 100ml + 10x 50ml + 4x 20ml)
- = 1.5 x 1580ml
- = 2370 ml/ 24 hours
- Encourage lots of oral hydration
- Severe: Morphine + Paracetamol + Ibuprofen or Diclofenac
- Moderate: Codeine + Paracetamol + Ibuprofen or Diclofenac
- Mild: Paracetamol/Ibuprofen
- ONLY IF no morphine available, give Pethidine as an alternative
- Sepsis (usually S. pneumo): Ceftriaxone
- Meningitis (usually S. pneumo): Ceftriaxone x 2 weeks
- Acute Chest Syndrome: Ceftriaxone
- Salmonella Osteomyelitis: Ceftriaxone (IV antibiotics for 2 weeks) then consider change to oral antibiotics (Ciprofloxacin). Aim for total duration of antibiotics 4-6 weeks
- Always check for Malaria parasites
- Cholelithiasis / Cholecystitis (>10yrs): AXR, abdominal ultrasound & surgical referral
- Iron overload secondary to Transfusion (less if not transfused)
- Stunted growth & Delayed maturation
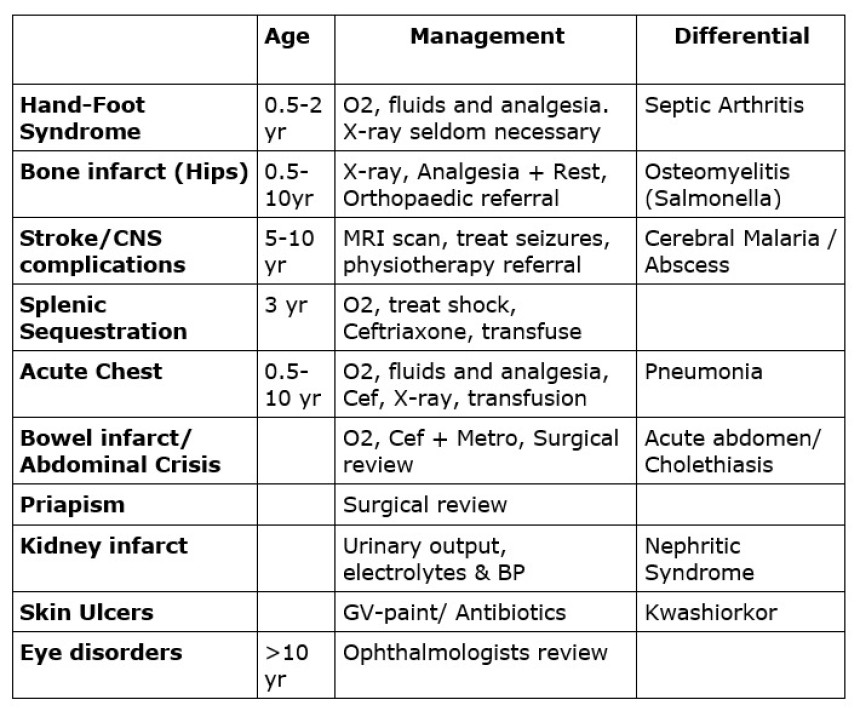 Discharge & Long-term follow-up
Discharge & Long-term follow-upSend to sickle cell clinic.
In QECH it takes place Tuesdays at 13:30 in Paediatrics Under 5 for:
- Malaria prophylaxis
- Sulphadoxine-Pyrimethamine (SP - Fansidar) once a month
- < 2years: 1/4 tablet
- 2 - 5 years: 1/2 tablet
- 5 - 10 years: 1 tablet
- 10 - 15 years: 2 tablets
- >15 years: 3 tablets
- OR Chloroquine 5 mg/kg once a week
- Folic Acid (1-5 mg daily)
- Benzathine-Penicillin (>6 months): Monthly IM <30kg: 600 000 IU; >30kg: 1 200 000 IU
- Pneumococcal vaccine (2 and 5 yrs) - if available
- Consider Hydroxyurea for those with frequent painful crises (discuss with senior)
- myelosuppressive agent - the only effective drug proven to
- reduces frequency of painful episodes
- raises level of HbF and haemoglobin level
- usually decreases the rate of painful episodes by 50 %
- also decreases the rate of acute chest syndrome episodes and blood transfusions by ~50 % (in adults)
- Initial dose 10 - 15 mg/kg/day OD
- Side effects includes neutropenia, bone marrow suppression, elevation of hepatic enzymes, anorexia, nausea, vomiting and infertility!
- Do Not Give Ferrous-Sulphate
- Instruct mothers and patients to
- ensure early (hyper) hydration & Paracetamol
- keep them warm and to promptly seek medical attention if:
- Severe pain, not controlled with Paracetamol and Ibuprofen
- Fast breathing
- Looking much more pale than usual
- High temperature
- Vomiting and Diarrhoea
- or anything else they are worried about





